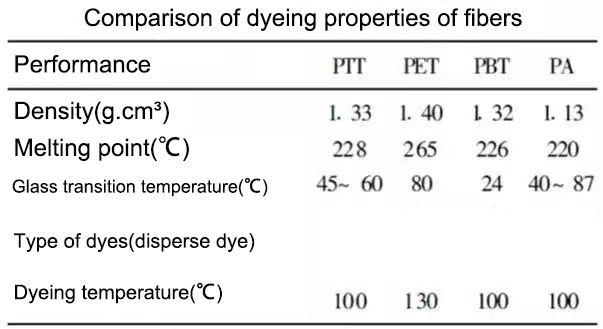
What is PTT fiber?
PTT fiber is the abbreviation of polypropylene terephthalate fiber, which is a new type of spinning polymer successfully developed by Shell Chemical (Shell Chemical Company) in 1995. PTT fiber, PET (polyethylene terephthalate) fiber and PBT (polybutylene terephthalate) fiber belong to polyester fiber and are spun from the same polymer. PTT fiber has the characteristics of both polyester and nylon. In addition to good antifouling performance, it is also easy to dye, soft to the touch, full of elasticity, and its elongation is as good as spandex fiber. Compared with elastic fiber spandex, it is easier to process and is very suitable for textiles. Clothing fabric;
Structure of PTT fibers
PTT is polytrimethylene terephthalate formed by polycondensation of 1,3-PDO and terephthalic acid, and its molecular structure is as follows:
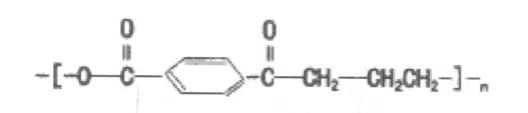
PTT is an aromatic polymer, which is generally made of 1,3-propanediol (PDO) and terephthalic acid (TPA) through melt polycondensation, and is produced by melt extrusion spinning in industrial production. Similar to filament and staple fiber, the production of PDO, an important raw material, is prepared by bio-enzyme catalysis, which reduces the production cost of PTT.
Structural comparison of PTT fiber with PET and PBT:
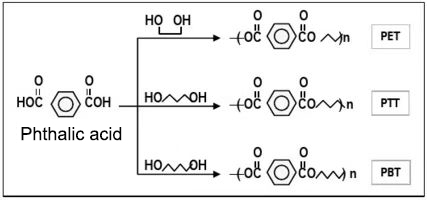
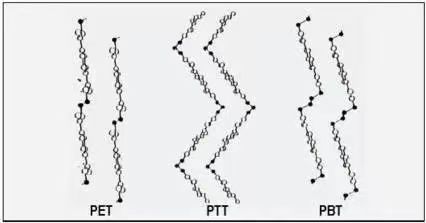
Preparation of PTT
The synthesis mechanism of PTT is similar to that of PBT and PET. It is a polyester resin obtained by polymerizing dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) or purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and 1,3-PDO. Similar to PET, its synthesis process can be roughly divided into direct esterification and transesterification.
Direct esterification method (PTA method):
The raw materials of the direct esterification method are PTA and 1, 3-PDO. This process is researched and developed by Zimmer Company and Degussa Company. Generally, the polymerization is divided into three stages, including three main stages of esterification of PTA and 1,3-PDO, precondensation and final polymerization. The polymerization end time of different reaction stages is distinguished by stirring. It is basically modeled on the polymerization of PET; while Zimmer uses a 5-stage continuous melting process (240°C-270°C) to make it. PAT and 1,3-PDO are esterified in the first two sections, and the excess PTA is removed from the second section; the third and fourth sections are pre-condensation reactors; the fifth section is the polycondensation reactor. The first three reactors are stirred-tank reactors, and the fourth and fifth stages use disc reactors developed by Zimmer. In order to combine with large-scale production, and the production cost of the PTA route is lower than that of the DMT route, no need to recycle methanol, the process is simple, and the cost is saved, so the direct esterification route is the focus of current research.
Transesterification method (DMT method):
Dimethyl phthalate (DMT) is transesterified with 1, 3-PDO. The transesterification method is carried out at a temperature of 140°C-220°C, using a Ti-based catalyst, first removing methanol, polycondensation, heating up to 270°C and reducing pressure to 5kPa Polycondensation, followed by polycondensation to obtain PTT.
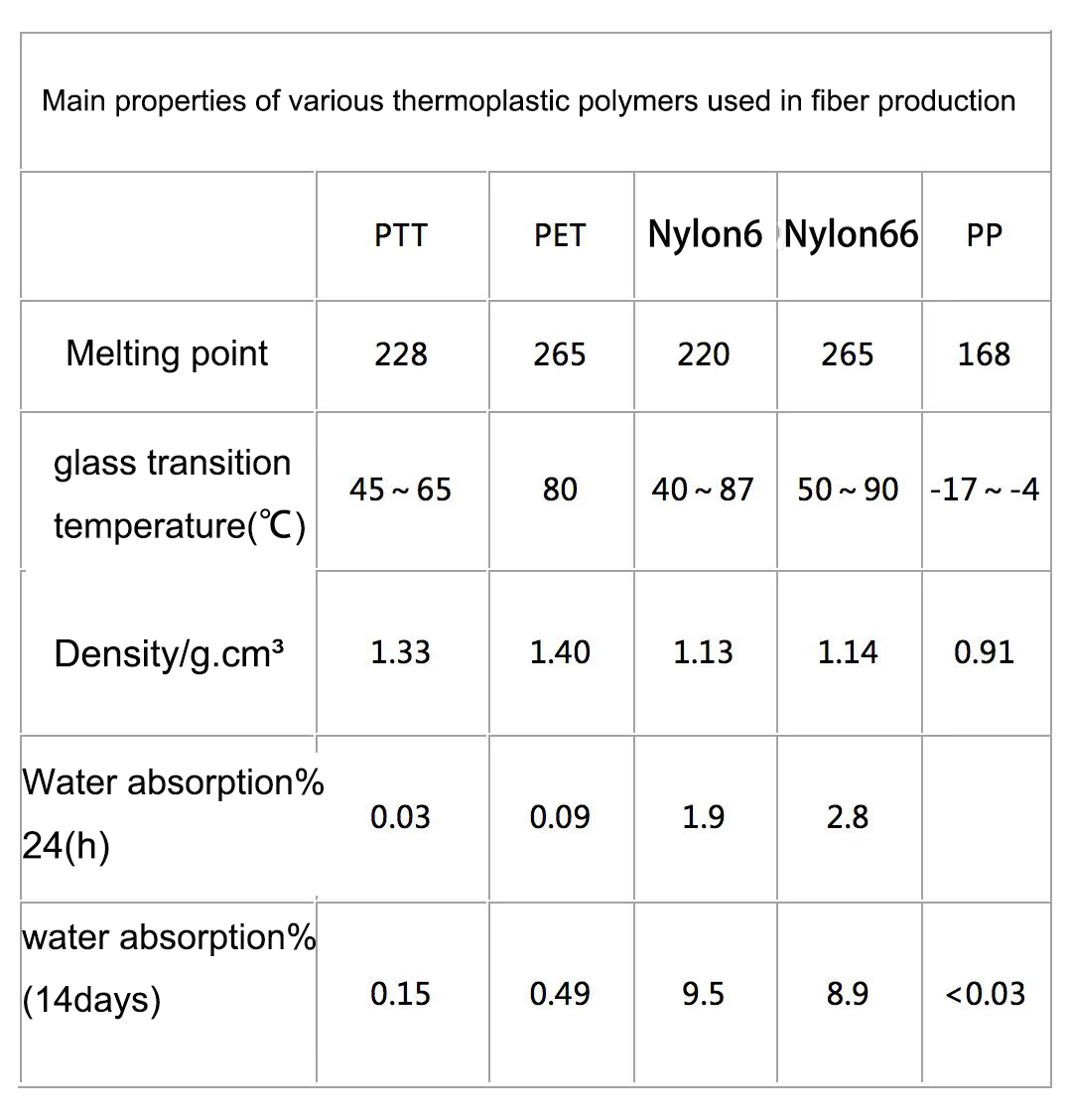
Properties of PTT fiber
good tensile resilience
The macromolecular odd carbon structure of PTT determines that the fiber has high elasticity and good elastic recovery rate. As far as stretched fibers are concerned, the relative breaking strength of PTT fibers is 20%~30% lower than that of PET (polyester). Tests show that: when the elongation at break is 25%, the relative breaking strength of PTT fiber is 3~3.5cN/tex, but higher than that of wool or cotton, so it can increase the strength of blended yarn when blended with cotton and wool. Another outstanding advantage of PTT fiber is its excellent tensile resilience.
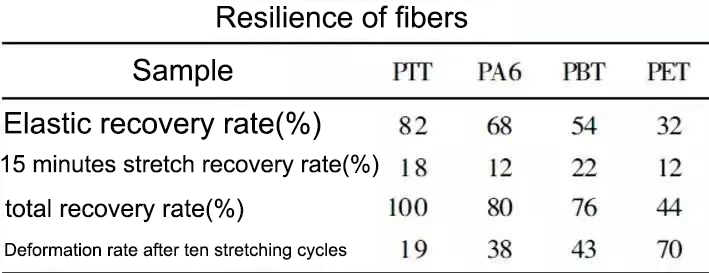
From the above table, it can be seen that the rapid elastic recovery rate of PTT fiber can reach 82% when it is stretched by 20%, and its elongation deformation almost returns to zero after being kept for 15 minutes, and the total elastic recovery rate is almost 100%, while PA, PBT, PET The total elastic recovery rates of the three fibers were 80%, 70% and 44%, respectively. Even after ten stretching cycles, PTT fiber still shows excellent resilience, which is not only higher than that of polyamide fiber (nylon) but also much higher than that of other polyester fibers.
Excellent dyeing performance
Compared with PET fiber, PTT fiber has obvious dyeability is one of its outstanding advantages. This is because the glass transition temperature of PTT fiber is 50~55°C, and it can be boiled at normal pressure without a carrier. At the same time, at the same dyeing temperature, the penetration depth of the dye in PTT is significantly higher than that of PET, and the color is uniform and the fastness is high. Blended fabrics with protein fibers such as wool and silk can be dyed in one-step co-bath method.
The fiber has a high degree of bulkiness
Due to the special molecular chain conformation and excellent tensile resilience of PTT fibers, highly fluffy BCT carpet yarns can be produced by hot air crimping and texturing. At the same time, the hand feel of PTT fiber has changed the relatively hard feeling of PET fiber, and the effect of fine denier PET fiber can be achieved without alkali reduction for dyeing and finishing. The fabric is soft and comfortable, which is better than PA (nylon).
Other performance
In addition to its particularly excellent softness and elastic recovery, PTT fiber also has excellent wrinkle resistance and dimensional stability, weather resistance, stain resistance, easy dyeing and good barrier properties, and can withstand gamma-ray sterilization. And improved stability against hydrolysis, so it can be used to develop advanced apparel and functional fabrics. The clothes made of it are comfortable to wear, soft to the touch, easy to wash, quick-drying, and non-ironing, which meet the requirements of people's fast-paced life. Its performance and elasticity, low static electricity, wear resistance and low water absorption are all better than nylon.
Use of PTT fiber
1.1 Original fabric → dyed finished fabric
(1) knitted fabric
For all kinds of knitted fabrics, desizing and washing treatments may generally not be required, and the fabrics may or may not be relaxed and preheat-set. Schematic diagram of the dyeing cycle and dyeing time of PTT fiber fabrics dyed with low-energy disperse dyes. Like the dyeing of PET fabrics, PTT fabrics can also be dyed with disperse dyes. The preferred dyeing temperature is 100-110°C. In order to obtain highly elastic and stretchable fabrics, it is necessary to heat-set the fabrics at a calibrated temperature. Fabric softeners can be added to dyed and heat-set fabrics to soften them, after which the fabrics are final heat-set at a temperature lower than or equal to the pre-heat-setting temperature. The resulting fabric should have good elasticity and soft hand feeling, and its quality is better than the original fabric.
(2) Woven fabric
Like PET woven fabrics, PTT woven fabrics may often require a sizing and desizing finish, with a dyeing process similar to that of knitted fabrics. In addition, preheat setting and soft finishing of PTT woven fabrics are optional, but the fabric must be final heat set.
1.2DTY→dyed yarn→dyeing and finishing fabric
Yarns made of PTT fibers can also be dyed, and the finishing process after dyeing is similar to the above-mentioned finishing process of knitted and woven fabrics.
2.1 Yarn→original fabric→dyed fabric
Using a process similar to the above, the spun yarn made of PTT staple fibers (single spinning or blending) can be knitted or woven into raw fabrics. During the weaving process, it is important to calculate the relatively high elasticity of PTT staple fiber compared to the elasticity of PET and polyacrylonitrile spun yarns.
The original fabric is dyed and finished in a process similar to the above, and various traditional textile techniques can be used to change the dyeing and finishing conditions of the fabric in order to calculate the elasticity and shrinkage of the PTT spun yarn. And it has been confirmed that various fabrics with elastic and non-elastic structures woven from PTT spun yarns have good properties, and the performance of the fabrics is also very good in various standard fabric tests including pilling. All kinds of textiles made of PTT spun yarn have an excellent hand feel, which is at least comparable to that of cotton fabrics and acrylic fabrics.
2.2 yarn → dyed yarn
In addition, various dyed yarns can be used to weave knitted and woven fabrics using similar processing methods as above.
Application of PTT fiber in nonwovens
The mixture of PTT staple fibers and other fibers, such as PET, nylon and polypropylene fibers, can be made into various nonwoven fabrics by needle punching and spunlace processing methods. The nonwoven fabrics made of these PTT staple fibers are characterized by hand feeling Nice and highly fluffy.
Due to the good elasticity and softness of PTT filaments and staple fibers, they are very suitable for the production of knitted and woven fabrics and all kinds of clothing made of these fabrics. PTT fibers are especially suitable for the market of textiles with high elasticity and soft touch. need.
In addition, low dyeing temperature and pressure and strong anti-fouling ability are other advantages of PTT fiber. PTT fiber is also a good candidate fiber in the field of nonwovens. Various nonwoven fabrics based on PTT fibers can also be manufactured by using PTT staple fibers (pure spinning or blending) and using needle punching or spunlace processing technology, or spunbond or melt blown methods. PTT fiber can also be used to make ultra-fine denier artificial leather. In addition, various nonwoven products made of PTT fiber as the basic raw material have two major advantages, namely, soft hand feeling and resistance to gamma ray radiation.
PTT fiber is a new type of product in the polyester fiber family. Compared with PET fiber, the glass transition temperature of PTT fiber is about 15°C lower. This fiber has the characteristics of both polyester fiber and polyamide fiber. In addition to strong stain resistance, its dyeing performance is better than polyester. Soft to the touch, it can be dyed and printed with common disperse dyes without using special chemicals.
The comparison of the chemical structure of PTT fiber and PET fiber is as follows:
- Do not use strong alkali for long-term high-temperature treatment (such as desizing and scouring), so as not to damage the elasticity of the fiber.
- The recommended dyeing conditions and recommended dyes for PTT fiber dyeing are as follows:
(1) Dyeing process (for light color)
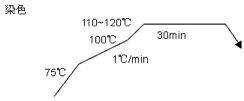

For medium and dark colors
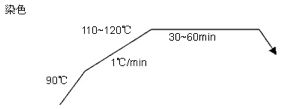

(2) Recommended dyes for PTT fiber
From the disperse dyes marketed as dyes for polyester fibers, dyes that satisfy both dyeability and color fastness are selected for dyeing. Even if it is the same disperse dye, compared with polyester fiber, it is slightly inferior in light fastness and wet fastness, so it needs to be paid attention to. All dyes for dyeing and washing are available, and the ternary colors are common.
(3) Dyeing method
It is most important to control the heating rate and slow heating. There are three aspects to pay attention to in PTT dyeing: color flower, oligomer, abrasion and wrinkle.
a. Color defect: mainly to control the heating rate.
b. Oligomers: The oligomers of PTT are about 4 times that of conventional polyester fabrics. Generally, alkaline dyeing at about 110-120 degrees is used, and the reduction cleaning process can also be omitted, which is the preferred low-cost method. Or use carrier dyeing to lower the dyeing temperature to about 100 degrees. The cost of carrier dyeing is higher than that of alkaline dyeing. Ordinary acid dyeing can be used to add oligomer remover, and after dyeing, the cost is also very high, and the oligomer remover is not ideal for the removal rate of oligomers produced by high temperature PTT fabrics, and there are hidden dangers in dyeing.
c. Scratches and wrinkles: Conventional anti-wrinkle softeners in the bath or smoothing agents such as Yuzhongbao basically have no effect on preventing PTT staining and scratches. Using alkaline dyeing can prevent scratches, if using conventional acid dyeing or carrier dyeing, high-grade in-bath anti-wrinkle smoothing and softening agents that are smooth, soft, and elastic at high temperatures are required.
3. The best temperature for shaping PTT fiber fabric is: 150~160℃*30s.




